/What to do (and not do)
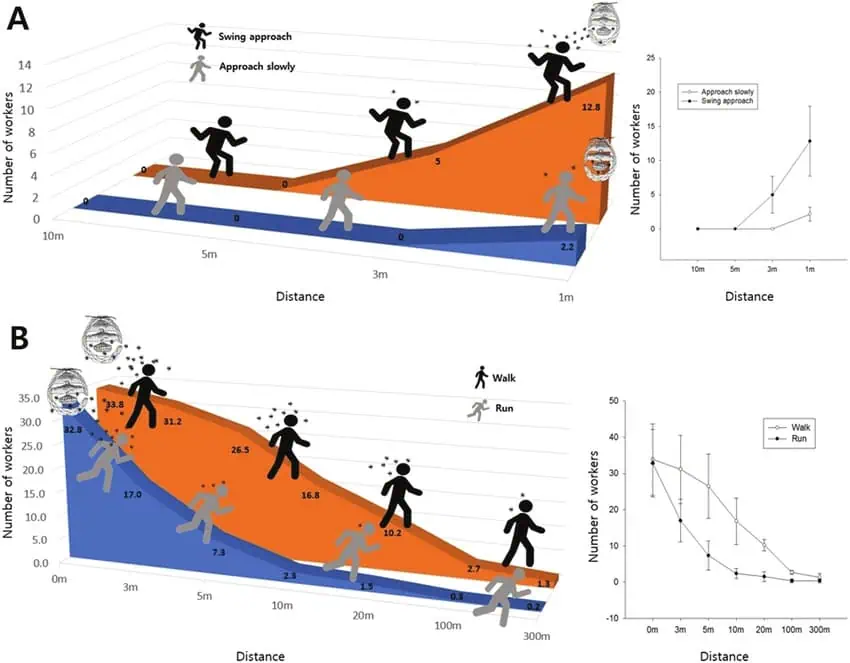
Distance of Vespa velutina defensive behavior
A: Comparison of the first attack distance when approaching by walking slowly or with swinging arms toward the nest.
B: Comparison of workers’ chasing distance when an intruder walks slowly or runs away when the wasps attack unexpectedly in front of the nest (source 1).
If you encounter an Asian hornet nest, your priority should be safety. Do not attempt to inspect or remove it yourself. Secondary nests can house thousands of hornets, and disturbance often leads to aggressive defensive behaviour. Instead, observe from a safe distance, taking note of the nest’s location and the hornets’ flight paths. This information can help authorities or trained professionals locate and manage the nest effectively.
Do not use pesticides, throw objects, or try to destroy the nest. Most incidents of stings and colony disruption occur during amateur removal attempts. Certified pest control teams or local invasive species authorities should handle any removal, using protective equipment and approved methods.
UNDER NO CIRCUMSTANCES TRY TO DESTROY THE NEST YOURSELF
Timing matters.
Early in the season, selective traps can target the founding queen, reducing the chance of the colony establishing for the year. Homemade trappings or chemicals can harm native insects, so intervention should be thoughtful.
Preventive measures in daily life also help reduce attraction: seal garbage bins, collect fallen fruit, and cover compost heaps. Share knowledge with neighbours and local beekeepers. The goal is containment and reporting, not confrontation. Following these steps increases the chance of safe, effective management.
Research by Choi, Hong, and Kwon (source 1) shows that yellow-legged Asian hornets workers respond more aggressively to dark colors and black hair, while loud noises alone are less likely to provoke an attack. This means that wearing lighter clothing and keeping a calm posture can reduce the risk of triggering defensive behavior during observation. By combining careful observation, attention to seasonal timing, and understanding of hornet sensitivities, people can contribute to early detection and control without putting themselves at risk.
The goal is not confrontation, but containment: by following these evidence-based guidelines, individuals can protect themselves, support professional control efforts, and help reduce the spread of this invasive species.